Hepatic lesion characterization in Fontan-associated liver disease: a single-center experience
Laura M. Hernandez Diaz MD1, Grant VanNess MD1, Sushmitha Srinivasan MBBS1, Roland C. Hentz MS3, Joel Hickman3, Nawras Habash MBBS2, Samar H. Ibrahim MBChB2, Sara Hassan MD2.
1Department of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States; 2Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Mayo Clinic , Rochester, MN, United States; 3Division of Clinical Trials and Biostatistics , Mayo Clinic , Rochester , MN, United States
Introduction: Liver lesions, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), are known complications of Fontan-associated liver disease (FALD). This study aims to assess the prevalence and outcomes of liver lesions in a single center cohort.
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted on patients who underwent Fontan surgery at Mayo Clinic from 1985 through 2014. Demographics, laboratories, imaging, and liver biopsies were analyzed, excluding patients with pre-existing liver disease.
Results: Of the 737 patients screened, 159 met inclusion criteria. Thirty-nine (24.5%) developed FALD-related liver lesions, 26 (67%) were male and 32 (84%) white. The average age at Fontan surgery was 3.7 years (range: 2.9–5.7), and the average age at liver lesion identification was 24.5 years (SD 7.7). Laboratory results at lesion identification showed normal transaminases in all patients, and normal direct and total bilirubin in 79% and 65%, respectively. All patients underwent liver imaging, with hepatic MRI with contrast performed in 30 (77%). Findings included nodules >1 cm in 77%, nodules <1 cm in 83%, splenomegaly in 43%, hepatomegaly in 40%, and ascites in 40%. Nineteen patients (50%) underwent targeted liver lesion biopsies, revealing focal nodular hyperplasia in 16%, adenomas in 11%, regenerative nodular hyperplasia in 5%, and HCC in 11%. One patient underwent transarterial chemoembolization (3%), one (3%) underwent liver transplantation, and two (5%) received heart transplants.
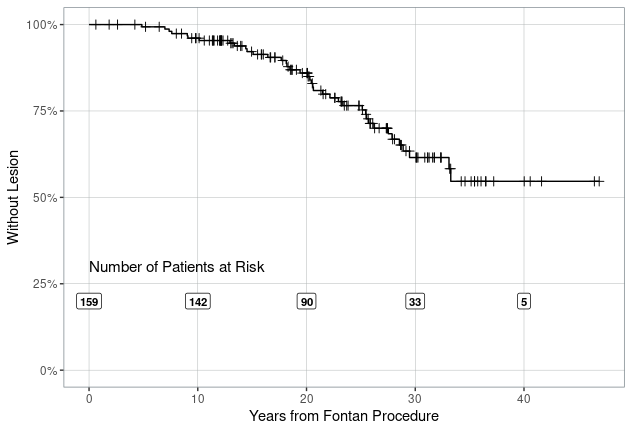
Conclusion: Estimated cumulative incidence of liver lesions was 38.5 % at 30 years in FALD patients. Two patients were diagnosed with HCC, underscoring the importance of monitoring with imaging and biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
The WebApp is sponsored by:

If you have any questions during the meeting, please go to the registration desk. Our emails will be monitored sporadically.
REGISTRATION DESK OPENING TIMES
Thursday, May 1, 2025, 07:00-17:30 Friday, May 2, 2025, 07:00-12:00